Wire Electrical Discharge Machines (EDMs) and Laser Cutting systems are viable options for tasks demanding precise tolerances. Employing sophisticated thermal technology with fine-point precision, both methods excel in cutting and molding various work materials. Nevertheless, notable distinctions exist between EDMs and lasers, influencing the optimal choice based on specific business needs.
This comparison between laser cutting and Wire EDM aims to elucidate the distinctive characteristics of each method, shedding light on their operational principles, material compatibility, and specific strengths. Ultimately, selecting the most suitable solution hinges on a thorough understanding of your particular requirements.
In essence, each process excels in distinct materials and applications. Laser cutting is effective for the most rigid materials, while wire EDM can cut through thicker materials. In this discussion, you will learn the disparities between Wire EDM vs. laser cutting to assist you in making an informed decision based on your needs.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a precision machining process that achieves accurate and intricate cuts through metal, plastic, and wood. This method involves concentrating a beam of light energy onto a specific point on the material’s surface, causing it to melt or vaporize. A gas jet then expels the melted material from the cutting path. Notably, metal cutting demands higher laser power than plastics and wood.
Although several laser-cutting technologies exist, the industry commonly employs fiber and CO2 lasers.
Benefits of Laser Cutting
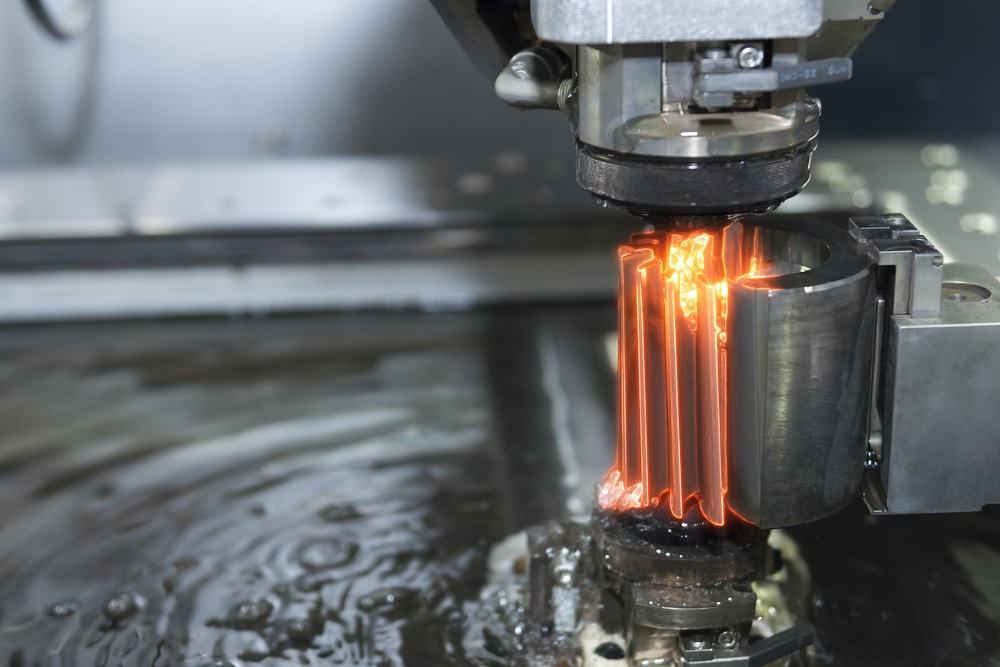

Precision and Detail Excellence
Laser-cutting technology delivers exceptional precision, creating intricate and highly detailed cuts. This precision proves advantageous in industries with stringent requirements for tight tolerances and intricate designs, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Versatility Across Industries
A key strength of laser cutting lies in its ability to handle a diverse range of materials. From robust metals like steel and aluminum to more delicate substances like plastics, wood, and fabrics, laser cutting is a versatile solution. This adaptability positions it as a fundamental technology across industries, including manufacturing, automotive, signage, and textiles.
Efficiency and Rapid Production
Renowned for its speed and efficiency, laser cutting significantly contributes to expediting production processes. This attribute is precious in industries where swift turnaround times are paramount, such as producing prototypes or meeting high-volume production demands.
Non-Contact Operation for Material Integrity
The non-contact nature of laser cutting minimizes the risk of material damage or contamination during the cutting process. This quality is pivotal, especially when working with delicate materials sensitive to physical contact or abrasion.
Automation for Consistent Quality
Laser-cutting machines seamlessly integrate into automated systems and are controlled through Computer Numerical Control (CNC). This automation enhances operational efficiency and ensures consistency and repeatability in cuts. It reduces the likelihood of errors, promoting overall product quality.
Cons of Laser Cutting
Substantial Initial Investment
Despite its many advantages, the initial investment required to acquire and set up laser-cutting equipment can be substantial. This financial commitment may challenge smaller businesses or startups seeking to adopt this technology.
Material Thickness Limitations
Laser cutting encounters challenges when dealing with highly thick materials, particularly certain metals. This limitation necessitates careful consideration when selecting the appropriate cutting method for specific applications.
Challenges with Reflective Materials
Highly reflective materials, such as certain metals, can pose challenges in laser cutting applications. The reflective nature of these materials may cause the laser beam to be reflected, potentially leading to inconsistencies in the cutting process.
Ongoing Maintenance Requirements
Laser-cutting machines demand regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Maintenance tasks can be intricate and time-consuming, and neglecting them may result in decreased efficiency or potential machine breakdowns, necessitating costly repairs.
Potential for Emission of Harmful Substances
Certain materials may release toxic fumes when subjected to laser cutting. Proper ventilation and safety measures are crucial to mitigate health and environmental risks associated with these emissions, adding a layer of consideration to the operational setup.
Types of Laser Cutting
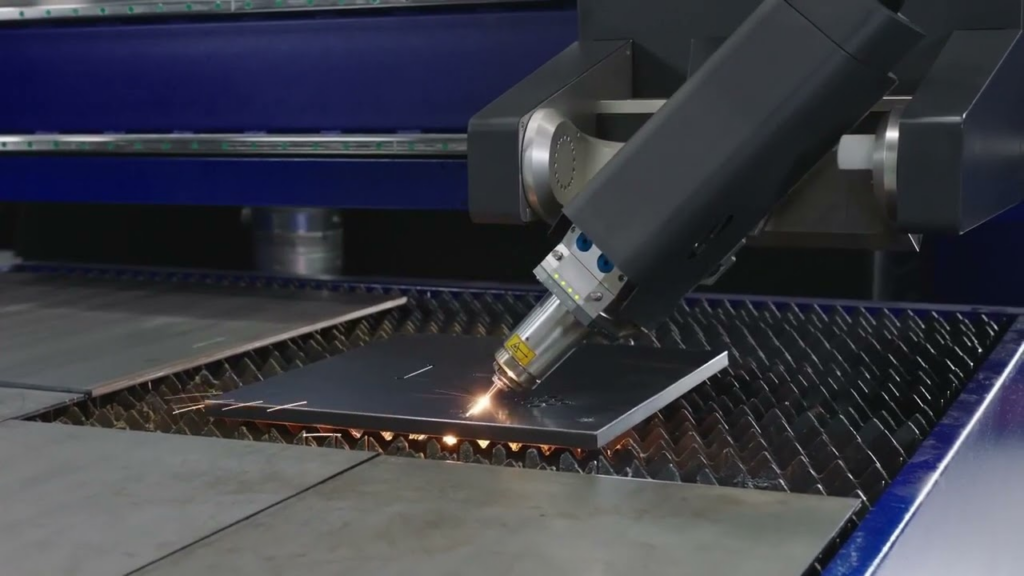

Various laser cutting methods are employed in the industrial sector, each customized for specific materials and applications. Here are the primary types of laser cutting utilized in various industries:
CO2 Laser Cutting
CO2 (carbon dioxide) lasers generate a beam through a gas mixture, typically containing carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and helium. Versatile CO2 lasers are well-suited for cutting non-metallic materials like wood, acrylic, plastics, and fabrics. They are also effective for thin metal sheets. It is extensively used in signage, textiles, and crafting intricate designs in non-metallic materials.
Fiber Laser Cutting
Fiber lasers employ optical fibers doped with rare-earth elements to generate a concentrated laser beam. It is ideal for precision cutting metals, including steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. It’s widely adopted in the automotive industry, aerospace, and metal fabrication due to its efficiency in working with metal materials.
Nd: YAG Laser Cutting
Nd: YAG lasers generate a laser beam using a crystal, typically Nd: YAG, and a flash lamp. It is suitable for cutting thicker metals, ceramics, and certain plastics. Nd: YAG is employed in specialized applications in the aerospace industry for cutting turbine blades and medical device manufacturing.
Disk Laser Cutting
Disk lasers use a rotating disk as the gain medium to generate the laser beam. It is effective for cutting thin to medium-thick metals with high precision. Disk laser cutting is commonly utilized in industries requiring high-speed and precision cutting, such as automotive production.
Pulsed Laser Cutting
Pulsed lasers deliver energy in pulses, allowing precise control over the applied energy. It is versatile and applicable to various materials, including metals, ceramics, and composites. A pulsed laser is used in applications where controlling heat input is crucial, such as producing electronic components.
Submerged Laser Cutting
Submerged laser cutting involves conducting the cutting process underwater or in a liquid environment. It is primarily used for metals to minimize heat-affected zones and enhance cut quality. Submerged laser cutting is applied in industries where minimizing thermal distortion and improving cut quality are critical, such as precision engineering.
What is Wire EDM Cutting?
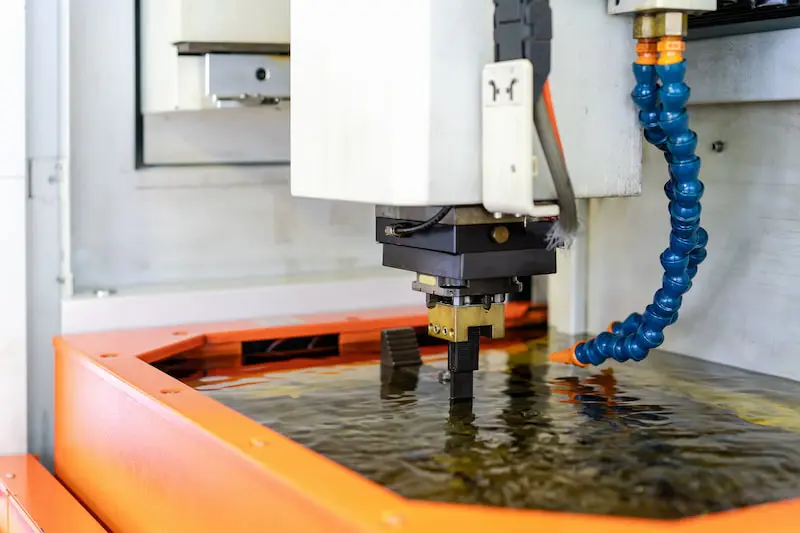

Wire EDM, or Wire Electrical Discharge Machining, is an advanced, non-contact subtractive manufacturing process. This technique uses an electrically charged thin wire immersed in a dielectric fluid to carve metal parts into diverse shapes.
This process is characterized by its ability to generate small chips and precise cut lines, achieved through the melting or vaporization of the material rather than traditional cutting methods. This unique approach allows for the machining of parts that are not well-suited for conventional machining techniques. It’s important to note that for Wire EDM to be effective, the components being worked on must possess electrical conductivity.
Advantages of Wire EDM
Wire EDM, or Wire Electrical Discharge Machining, offers several notable advantages:
Precision and Accuracy
Wire EDM excels in producing precise and accurate cuts, eliminating the need for additional processing and finishing of the workpiece.
Complex Designs and Shapes
This process is well-suited for creating complex designs and shapes that may pose challenges for traditional CNC machining methods.
Versatility in Machining
It proves highly applicable in machining small parts and cutting highly detailed items that might be too delicate for other machining options.
Ideal for Fragile Materials
Wire EDM machining is particularly suitable for fragile materials that cannot withstand the stress of other machining techniques.
Burr-Free and Distortion-Free
With a single processing stage, Wire EDM ensures materials are cut without leaving burrs or causing distortion.
Continuous Cutting Process
The machining process operates continuously without interruptions. Even if the wire breaks during cutting, the process resumes immediately.
Disadvantages of Wire EDM
Despite its strengths, Wire EDM also presents certain limitations:
Limited Material Compatibility
Wire EDM is only compatible with materials that conduct electricity, limiting its application to electrically conductive substances.
Oxide Layer Development
Some materials, like aluminum, may develop an oxide layer on the cut surface, necessitating additional finishing processes and raising the overall cost.
High Initial Investment and Maintenance Cost
Implementing Wire EDM involves a substantial initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs, which may be perceived as a drawback compared to other machining methods.
Key Components of a Wire EDM Machine

A Wire EDM machine, a sophisticated tool in modern manufacturing, integrates various components to execute precise material shaping. Understanding each component is crucial for optimizing the machine’s performance. Here’s an in-depth exploration of these critical elements:
CNC Tools
At the heart of Wire EDM machining, CNC tools are pivotal in orchestrating the entire operation. These tools not only control the sequencing of the wire path but also automate the cutting process. The level of sophistication in CNC tools directly influences the error margin and the overall machining time, making their selection a critical aspect of machine operation.
Power Supply
The power supply unit delivers controlled pulses (100V to 300V) to the wire electrode and the workpiece. This component regulates the frequency and strength of the electrical charges passing through the Wire. A highly advanced power supply unit is imperative to ensure precision and quality in Wire EDM machining.
Wire
Serving as the electrode for electrical discharge, the Wire’s diameter is intricately tied to the shape and thickness of the workpiece. Different wires are employed in Wire EDM machining, each with specific attributes:
- Brass Wires: Recognized for excellent conductivity, the zinc content influences cutting speed. However, a balance must be maintained to avoid corrosion.
- Zinc-coated Wires: Surface-coated with pure zinc or zinc oxide, enhancing machining speed.
- Diffusion-annealed Wires: Produced through a process involving layers of pure zinc, ideal for mass production.
Selecting the right wire material involves considering factors such as tensile strength, fracture resistance, conductivity, vaporization temperature, and hardness.
Dielectric Medium
In the wire-cut EDM process, a tank is filled with a dielectric fluid, commonly deionized water. This fluid serves a dual purpose – preventing tiny particles from adhering to the wire electrode and ensuring a clean machining process. Additionally, deionized water acts as a cooling agent, contributing to an optimal surface finish on the workpiece.
Electrodes
The electrodes in the Wire EDM machine consist of the Wire (cathode) and the workpiece (anode). A servo motor meticulously controls the wire electrode’s movements, ensuring a safe distance from the workpiece throughout the cutting process. This meticulous control prevents unintended contact, safeguarding precision and accuracy in machining.
What are the Differences Between Laser Cutting and Wire EDM?
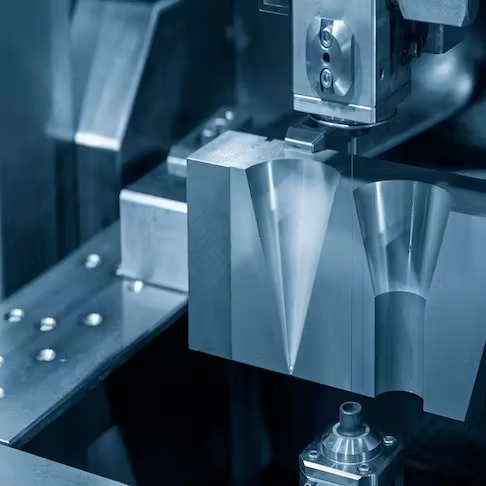
Among the advanced methodologies, Laser Cutting vs. Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) stand out as frontrunners, each boasting distinctive characteristics, applications, and advantages. This extensive comparison aims to dissect these two cutting-edge techniques, delving into their operational principles, applications, material compatibility, precision, efficiency, and cost considerations.
Operational Principles
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting harnesses the concentrated power of a laser beam to meticulously slice through materials. This non-contact process involves directing the laser onto the material’s surface, causing it to either melt or vaporize. The precision of the cut is intricately controlled by the focused laser beam’s intensity and movement.
During the operational phase, both Wire EDM and Laser Cutting uses CNC control; however, it’s essential to note that Wire EDM is a vital process within CNC machining, whereas Laser Cutting represents a distinct process within sheet metal fabrication.
Wire EDM
Conversely, Wire EDM relies on the principle of electrical discharge to achieve precision cuts. The cutting tool is an electrically charged thin wire submerged in a dielectric fluid. The controlled movement of the Wire, guided by CNC tools, facilitates intricate shapes and designs.
Material Compatibility
Laser Cutting
Exhibiting unparalleled versatility, laser cutting accommodates an extensive range of materials. Metals, plastics, composites, and even non-metallic substances succumb to the precision of the laser beam, positioning laser cutting as a go-to solution across diverse industries.
Wire EDM
Wire EDM excels in intricate designs and delicate materials and is tailored for electrically conductive materials. However, its material compatibility is limited to those capable of conducting electricity, making it ideal for specific applications rather than broad material versatility.
Precision and Intricacy
Laser Cutting
Renowned for precision, laser cutting excels in delivering intricate designs and fine details. The non-contact nature of the process ensures minimal material wastage, contributing to the meticulous execution of even the most complex geometries.
Wire EDM
Taking precision to another level, Wire EDM is particularly adept at crafting intricate shapes and designs. Its non-mechanical approach minimizes stress on delicate materials, ensuring consistent precision without compromising the integrity of the workpiece.
Efficiency and Speed
Laser Cutting
Operating at high speeds, laser cutting proves efficient for large-scale production scenarios. The rapid and precise cutting mechanism enhances productivity, making it an ideal choice for industries requiring swift turnaround times.
Wire EDM
While Wire EDM is precise, its cutting pace may be slower. However, the continuous machining capability without interruptions, even during wire breakage, contributes to overall operational efficiency.
Heat Generation
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting generates more heat than Wire EDM. While advantageous for some materials, it can be a drawback for substances sensitive to heat-induced distortions.
Wire EDM
Wire EDM’s minimal thermal stresses make it suitable for materials that can’t withstand the heat generated by laser cutting. This characteristic ensures the integrity of delicate workpieces.
Cost Considerations
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting often boasts lower initial setup costs, making it attractive for projects with budget constraints. However, ongoing maintenance and consumable costs should be factored into the overall expenditure.
Wire EDM
Despite potentially higher initial investment costs, Wire EDM can prove more cost-effective over time due to the longevity of the wire electrode and reduced maintenance requirements. This cost-efficiency becomes evident in scenarios requiring prolonged and consistent precision.
Applications
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting has extensive applications across the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and jewelry manufacturing industries. Its versatility makes it suitable for various materials and diverse production requirements.
Wire EDM
Wire EDM shines in applications demanding intricate designs, tight tolerances, and delicate materials. Industries like tool and die manufacturing, aerospace components, and medical device production benefit from its precision.
Here’s a table highlighting the key differences between Laser Cutting and Wire EDM:
| Criteria | Laser Cutting | Wire EDM |
| Operational principle | Uses a concentrated laser beam to cut materials. | Utilizes an electrically charged thin wire for cutting. |
| Material Compatibility | Versatile, suitable for a wide range of materials. | Primarily for electrically conductive materials. |
| Precision and Intricacy | Precise can handle intricate designs and fine details. | Exceptionally precise, excelling in complex shapes. |
| Process Efficiency | High-speed operation is efficient for large-scale production | Continuous machining capability for uninterrupted operation. |
| Heat Generation | generates more heat, a potential concern for heat-sensitive materials. | Minimal thermal stresses, suitable for delicate materials. |
| Cost Considerations | Lower initial setup costs and ongoing maintenance expenses. | Potentially higher initial investment, cost-effective over time. |
| Applications | Diverse applications across industries, including automotive and electronics. | Ideal for tool and die manufacturing, aerospace components, and medical devices. |
Conclusion
Wire EDM and laser cutting are robust methods, each excelling in specific aspects of material cutting. Considering the advantages of Wire EDM and laser cutting is crucial in selecting the optimal process for your particular application. It’s essential to comprehend the strengths and limitations of each method.
Zintilon specializes in precision wire EDM services tailored to various industries. Our expertise spans manufacturing, medical, electronics, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, food processing, government, energy, and telecommunications, ensuring precise and customized solutions for various applications.
FAQs
What is the fundamental difference between Laser Cutting and Wire EDM?
Laser Cutting: Utilizes a concentrated laser beam to melt or vaporize materials for precision cutting.
Wire EDM: Relies on an electrically charged thin wire submerged in a dielectric fluid to achieve high-precision cuts through electrical discharge.
Which materials are suitable for Laser Cutting and Wire EDM?
Laser Cutting: Versatile and suitable for various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Wire EDM: Primarily designed for electrically conductive materials.
How do the precision levels compare between Laser Cutting and Wire EDM?
Laser Cutting offers precision but may have limitations in intricate shapes. On the other hand, Wire EDM excels in achieving intricate shapes and fine details with high precision.
What industries benefit the most from Laser Cutting and Wire EDM services?
Laser Cutting is applied in diverse industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and jewelry manufacturing. In contrast, Wire EDM is preferred in industries requiring intricate designs and tight tolerances, such as tool and die manufacturing, aerospace components, and medical device production.



